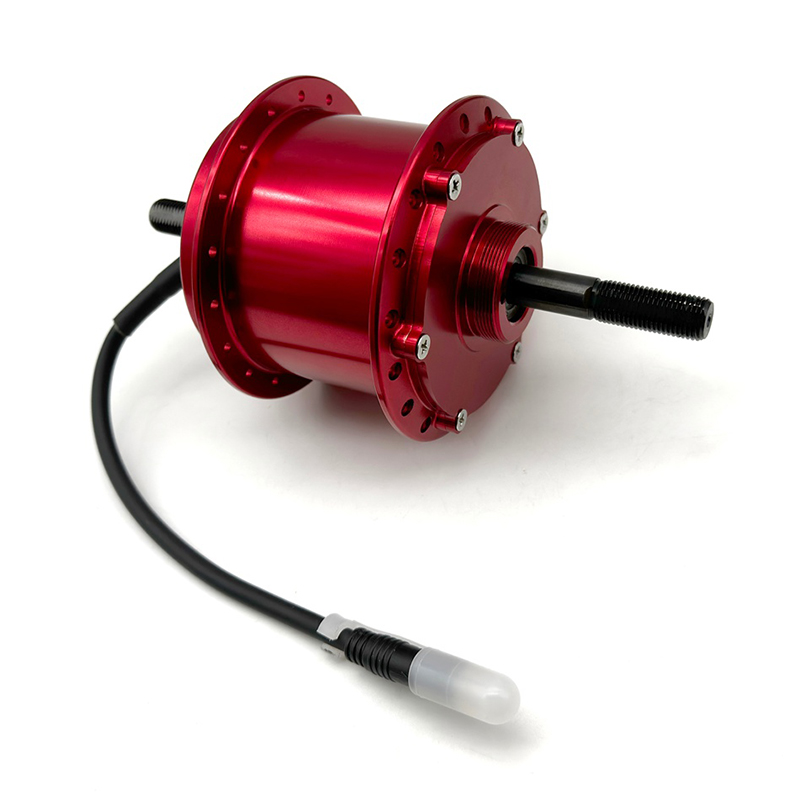
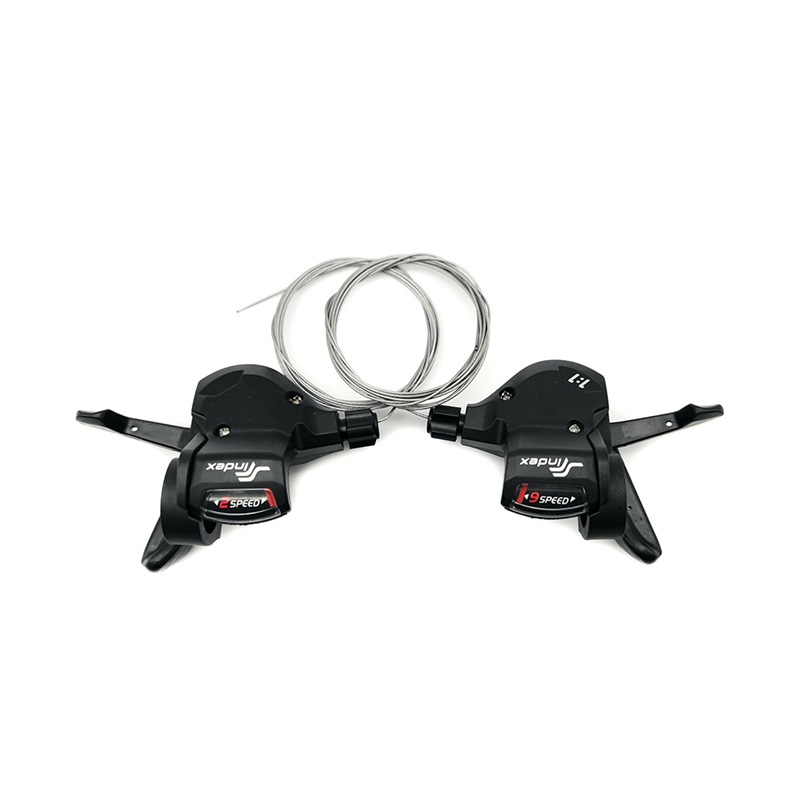
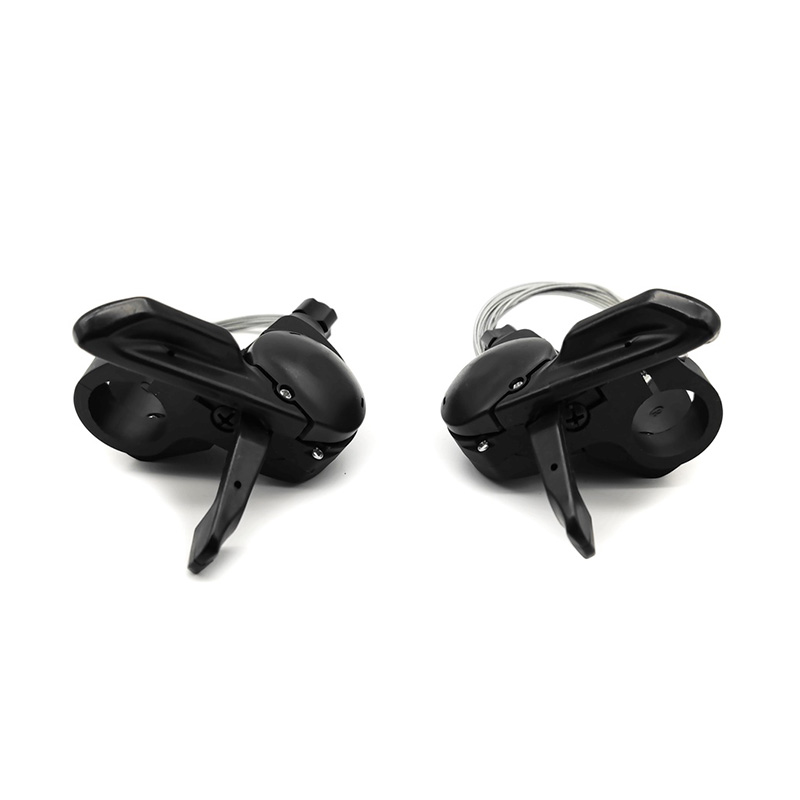
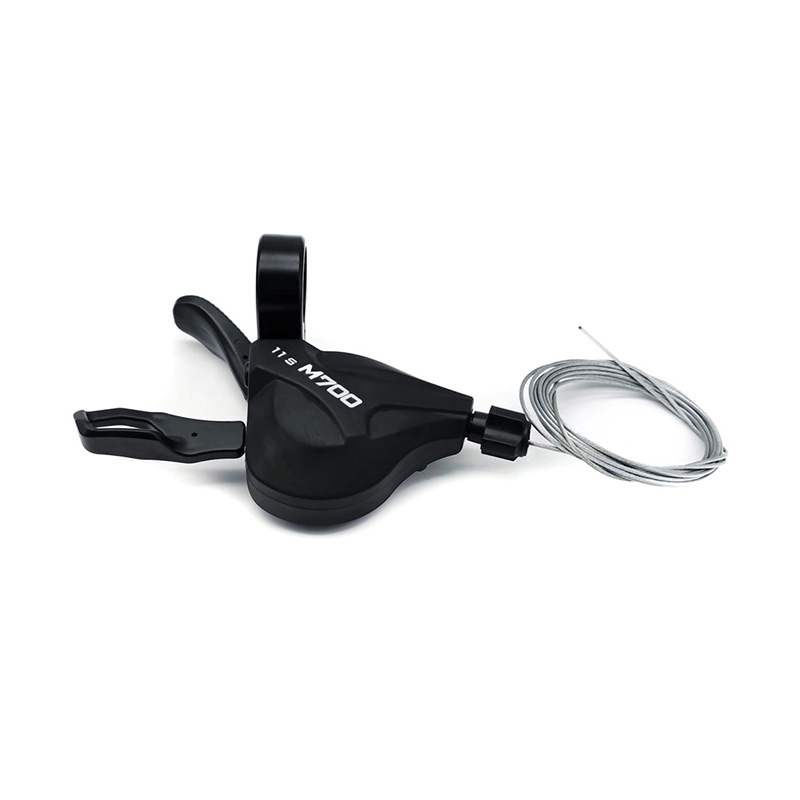
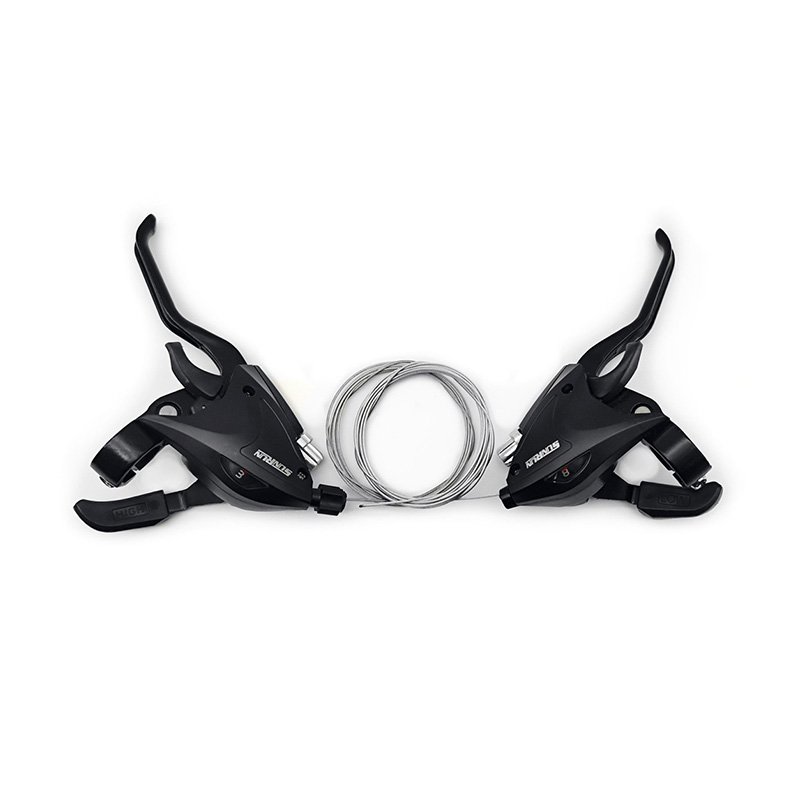
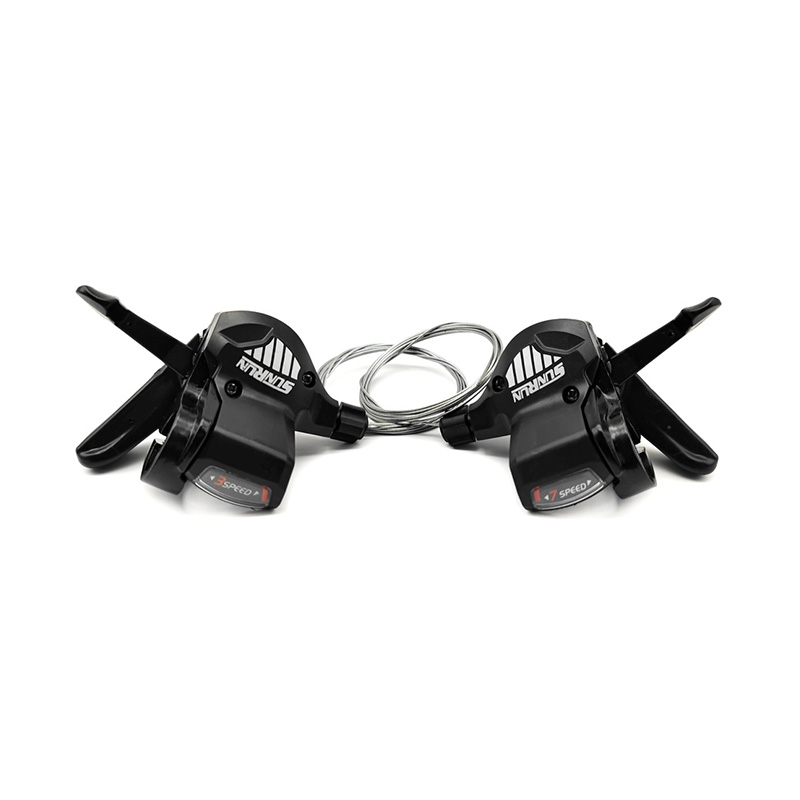
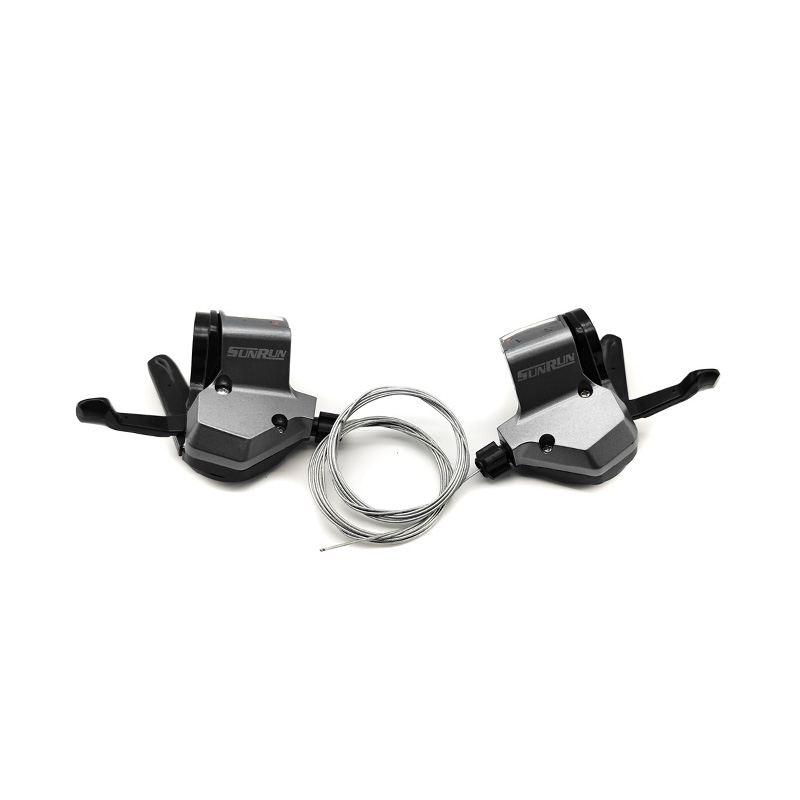
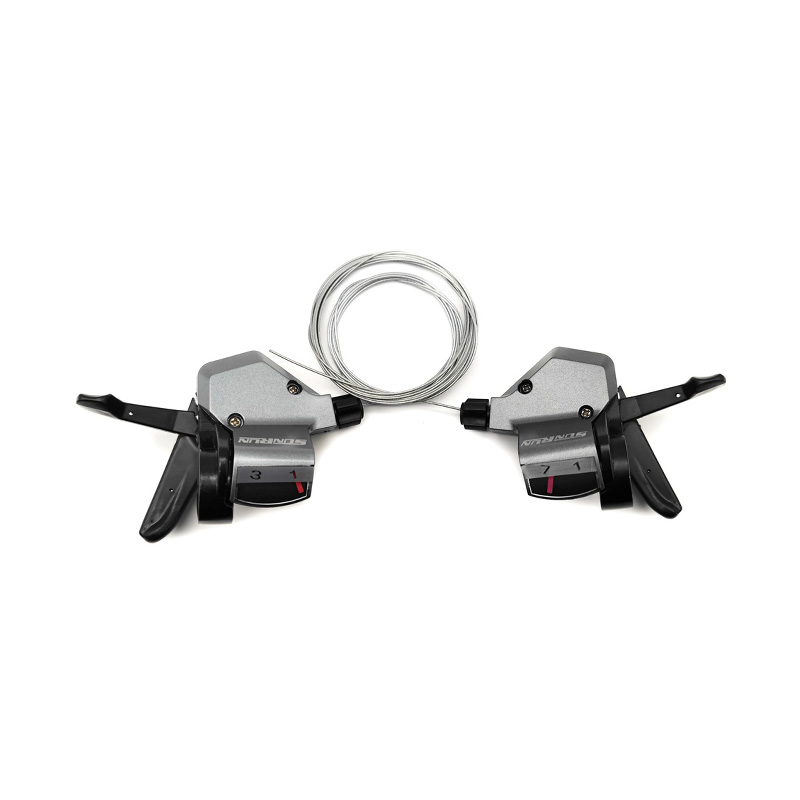
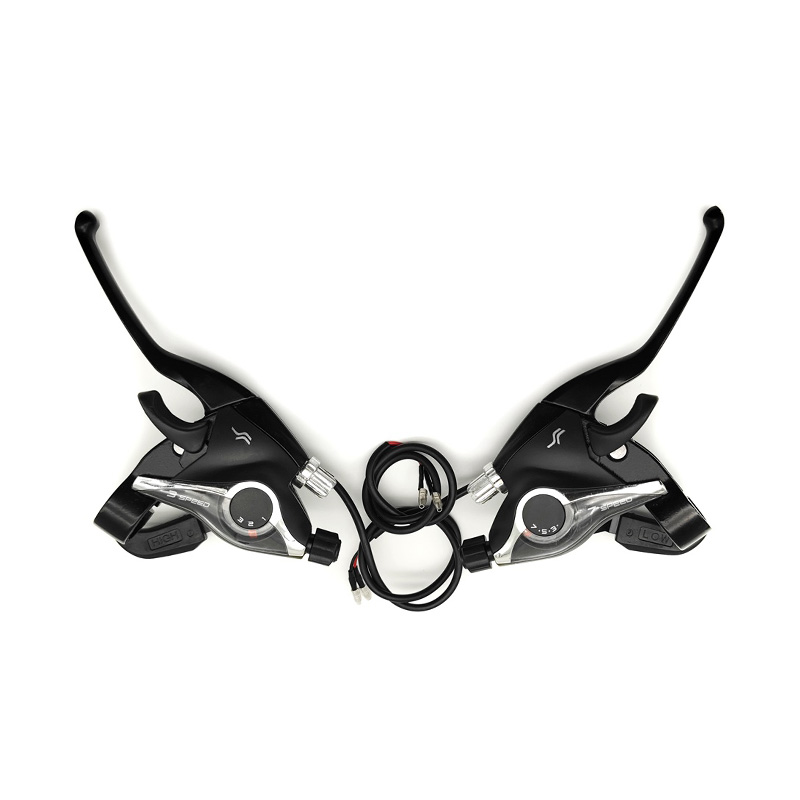
The performance of Pedal Assist E-Bike Kit Controller is closely related to sensor compatibility, because sensors directly affect the sensitivity, smoothness and riding experience of the power assist. The compatibility between different types of sensors and controllers determines the overall performance of the system.
Pedal-assisted e-bike systems usually rely on a variety of sensors to detect riding status, mainly including speed sensors, cadence sensors, torque sensors and combination sensors. Speed sensors are usually based on Hall effect or reed switches, and calculate riding speed by detecting the number of rotations of the wheel or crank. They have high compatibility and are supported by most controllers, but they need to match pulse signals and voltages. Cadence sensors detect the frequency of pedal rotation and are more versatile, but some low-end controllers may only support fixed pulse modes and need to be adjusted through jumpers or software. Torque sensors provide a more natural power assist experience by measuring pedaling force, but the controller needs to support analog signals or digital protocols, and there may be signal interference issues. Combination sensors are usually used in high-end systems and require controllers to support multiple signal inputs or dedicated communication protocols.
The compatibility of sensors and controllers mainly depends on signal type, communication protocol and mechanical interface. In terms of signal type, analog signals require the controller to have an ADC module, while digital signals have stronger anti-interference capabilities, but require protocol matching. In terms of communication protocols, general protocols have better adaptability, while private protocols usually require dedicated controllers or protocol decoders. In terms of mechanical interface, the middle shaft torque sensor needs to match the specifications of the bicycle's five-way bracket, while the wheel speed sensor needs to adapt to the spoke or disc brake installation position. In addition, the power supply voltage and signal filtering capabilities will also affect stability.
If you encounter sensor compatibility issues, you can solve them through hardware adaptation, software configuration and troubleshooting. In terms of hardware, you can use signal conversion modules or protocol gateways to match different interfaces. In terms of software, you need to calibrate the sensor parameters through the host computer software that comes with the controller, and optimize the filtering algorithm to reduce signal jitter. When troubleshooting, if signal loss occurs, you need to check whether the wiring is correct; if the power assist is not linear, you may need to recalibrate the zero point and sensitivity of the torque sensor. For high-end systems, you also need to ensure that the protocol frame format matches.
 中文简体
中文简体 English
English